March has been a weather roller coaster coming off a weekend with arctic chilling temperatures and snow into more typical spring conditions. Continue reading
Category Archives: Corn
Vine and Grass Control in Corn
Last August and September many were disappointed in the grass and vine infestations present at corn harvest in some fields. Often, these weed infestations emerged after PRE applied or early POST applied herbicides had played out. Continue reading
Burndown Time in Tennessee
It is now “burndown time in Tennessee.” The combination of supply chain issues with the ever-increasing presence of herbicide resistant weeds has made burndown time more of a challenge in 2022. Poa and ryegrass are two very common grass weeds and are of most concern, particularly before corn planting. Continue reading
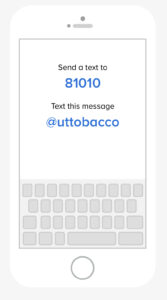
Remind Text Message System For Field Crops
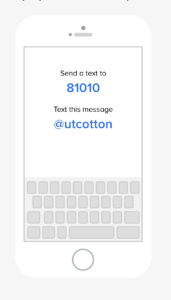
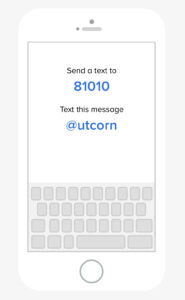
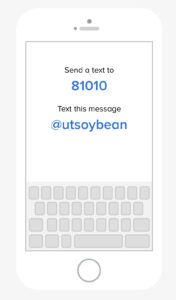
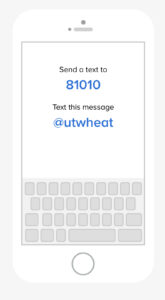
UT is implementing a new method of sending information to agricultural professionals. Remind is texted based communication system that facilitates information delivery via text or push notification. Messages are limited in length and recipients can directly message senders with questions. Enrolling is free and easy and takes less than a minute. Follow the instructions below to enroll in a crop specific class (cotton, corn, soybean, wheat or tobacco).
Dyersburg Grain Conference Still On for Thursday Feb 3
The West TN Grain Conference will be held on Thursday, Feb 3rd with a revised program that will allow attendees to return home earlier in the day. Attendees are advised to use their best judgement when traveling, as some areas may have more or less freezing rain and accumulation. Parking at the fairgrounds is likely to be muddy due to recent rains.
Registration will begin at 7:45 am with presentations starting at 9 am. The conference will wrap up at noon followed by a rib and chicken meal that can be eaten on-site in the Armory building or taken to-go. Travel safely, and we hope to see you in Dyersburg!!
Pre-registration Option for Upcoming Grain Conferences
Pre-register now to avoid waiting in line at two upcoming grain conferences in Tullahoma and Dyersburg scheduled for next week. Continue reading
In-person Grain Conferences Planned for 2022
Happy New Year!! The University of Tennessee will host three in-person grain and soybean conferences during 2022 and preregistration is currently ongoing. Continue reading
2021 Corn Grain Hybrid Tests in TN – Now Available
Results from the 2021 TN corn grain hybrid trials are now available at search.utcrops.com/corn-grains. Seventy-one hybrids were evaluated in small plot replicated trials (REC) at seven locations and fifty-four hybrids were evaluated in ten to twenty locations as non-replicated large strip plots (CST). A summary of hybrids that were in the “A group” (not statistically different from the top yield within each test) in either the REC or CST trial is given below. Continue reading