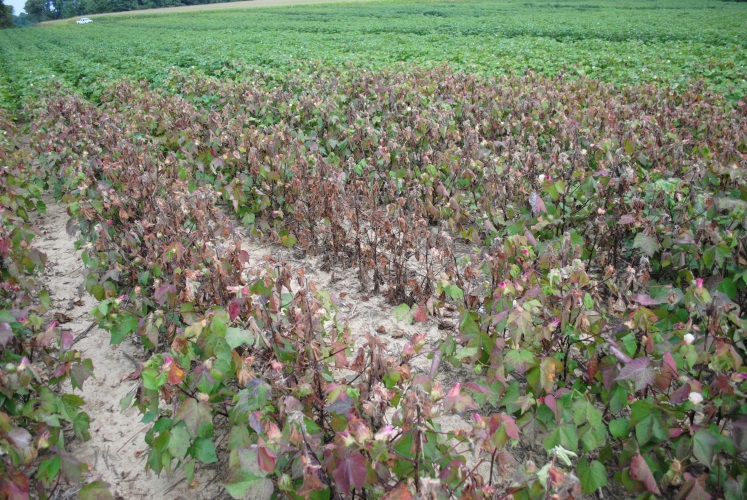
I have visited several fields in the past few weeks to examine circular/slightly irregular areas characterized by wilt, severe necrosis and death. After visiting with several other specialists, it is our consensus that these injured areas were caused by lightning. Although no action can be taken to bring injured plants out of the stress, additional information on plant symptoms may help you properly diagnose the stress and reduce the amount of ‘flak’ directed at your sprayer operator.
Several strong storms have made their way through the area over the past month, but I think much of the damage I’ve seen was caused by a system that moved through 14 July 2014. A radar snapshot of this system can be found below. I’m certain the system which moved through late last week and into the past weekend also damaged a few areas, as did systems that moved through on the 23rd of July. Although this isn’t an issue many cotton producers in the western states experience, lightning is very much a part of our afternoon, pop-up thunderstorms.
 Individual plant injury characteristics and shape of the affected area can vary substantially and are a function of a number of factors, including surface and subsurface soil moisture contents, strength of bolt, and plant biomass, among other things. Without delving too far into the physics of the strike, the large concentration of ion-containing water in the cotton stalk makes a far-better conductor than the lower-water content soil. Subsequently, the strike passes through the plant to ground the negative charge. As the negative bolt approaches the plants, streamers, or positive electric channels, form through plants near the negative bolt. This transfer of charge, through several different mechanisms, disrupts cell membranes and causes cell death.
Individual plant injury characteristics and shape of the affected area can vary substantially and are a function of a number of factors, including surface and subsurface soil moisture contents, strength of bolt, and plant biomass, among other things. Without delving too far into the physics of the strike, the large concentration of ion-containing water in the cotton stalk makes a far-better conductor than the lower-water content soil. Subsequently, the strike passes through the plant to ground the negative charge. As the negative bolt approaches the plants, streamers, or positive electric channels, form through plants near the negative bolt. This transfer of charge, through several different mechanisms, disrupts cell membranes and causes cell death.
So how does this affect the plant, and what does it look like?
A number of observations can guide you to diagnosing injury from lightning. First, the affected area will generally encompass an area less than 50’ in diameter. Although the affected area generally resembles a circle, these areas can be misshapen as a function of the factors mentioned above. Typically wilt will occur very rapidly with the plants in the center of the region being most affected.
Immature areas of each plant are generally the first to show signs of injury and are often dead within days. The apical meristem (plant apex) of almost all affected plants will die very quickly and the stem immediately below the growing point may be twisted or hooked so severely the meristem may be pointing towards the ground. Some affected plants may remain alive but commonly express symptoms of a severe abiotic stress (boll shed, leaf reddening, wilt). Damaged vascular tissue will appear brown. ‘Blow out’, or a vertical lesion or scarring, may be noted roughly 5-6 nodes down from the meristem and encompass several internodes. As previously mentioned, these symptoms do vary substantially from strike-to-strike.
 Although there is no method to save these injured plants, these areas should serve as testaments to the potential dangers of lightning. This is of particular importance now that chopping crews have again become a fairly common method of combatting weeds.
Although there is no method to save these injured plants, these areas should serve as testaments to the potential dangers of lightning. This is of particular importance now that chopping crews have again become a fairly common method of combatting weeds.
Additional information on lightning strikes and safety can be found at http://www.lightningsafety.noaa.gov/.



