Plant bug populations began to blossom this past week in some fields with average counts being reported up to 20-30 per drop cloth. However, populations remain below the recommended treatment threshold in many fields, and this shows the value of scouting. Stink bugs are also present in many fields, but again, populations vary considerably. To top it off, we are
seeing a large bollworm moth flight across parts of the state, and it is marching northward. So things are happening quickly. Moths and eggs are being observed in larger numbers in many fields, but moth trap catches are all over the board.
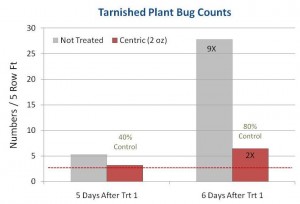
Get out your drop cloth! I suggest you start relying more heavily on the drop cloth. I’ve been in a number of fields this week where the sweep net “missed” populations of immature plant bugs. Sweep nets were indicating below threshold populations, but nymphal counts on drop cloths were above recommended treatment level (3 or more tarnished plant bugs per drop). The drop cloth is a better tool for sampling immature plant bugs. Nymphs will typically compose the majority of the population in blooming cotton, especially once you get two or more weeks past first flower. I’ve also had a few reports where good treatments appeared to fail. This seems to be occurring in the same areas where plant bug numbers have jumped. Even good treatments can appear to fail when populations are exploding. I’ve included a graph below from a test done last year in Jackson. You can see that tarnished plant bug numbers increased after two treatments (in this case Centric at 2 oz). What you can also see is that populations increased too much higher numbers in untreated plots. In this example, the “failed” insecticide applications actually provided 75-80% control after two applications.
We have cotton ranging from first bloom to approaching cutout (NAWF=5). Be sure you document when fields reach physiological cutout (NAWF=5). Insecticide applications for many pests such as plant bugs, stink bugs and bollworms can be terminated once you accumulate 350 DD60’s (usually around 18-22 days) after NAWF=5 is reached.
It is time to start utilizing tank mixes that include a pyrethroid insecticide in cotton that is blooming heavily. The table below is a list of potential tankmix or premix options. When plant bug pressure is high you should expect to make two consecutive applications on a 5 day schedule. At least one of these applications should probably include a pyrethroid partner to provide “insurance” against bollworms that will likely be present. Bt cotton and especially WideStrike varieties such as PHY375 WRF can sometimes require an insecticide application (typically a pyrethroid) for control of escaped bollworms. Besides, tank mixes that contain a pyrethroid insecticide often enhance control of plant bugs and stink bugs.
Some preferred treatment options for a pest complex in blooming cotton.
| Treatment | Rates per acre | Comments |
| Pyrethroid* + Bidrin | Mid to high rate + 2-4 oz | Bidrin XP II is a premix of bifenthrin and Bidrin. It is labeled at use rates of 8-12.8 oz/a, with 10 oz/a being a good starting point. |
| Pyrethroid* + Orthene (acephate) | Mid to high rate + 0.33-0.5 lb ai | Use 0.5 lb for heavy plant bug pressure . |
| Pyrethroid* + Vydate | Mid to high rate + 6-8 oz | |
| Pyrethroid* + Diamond | Mid to high rate + 4-6 oz | Prefer this treatment in combination with Bifenthrin to improve control of adults. Good choice in traditionally high pressure environments. |
| Pyrethroid* + Dimethoate 4E | Mid to high rate + 6-8 oz | |
| Pyrethroid* + Lorsban 4E or Nufos 4E | Mid to high rate + 8-12 oz | Cobalt Advanced is a premix of gamma-cyhalothrin + Lorsban. Recommended use rates range from 24-32 oz/a. |
| Endigo ZC (premix of Karate and Centric) | 4-5 oz | See comments below concerning resistance management. |
| Brigadier (premix of bifenthrin and imidacloprid) | 5.1-7.7 oz | See comments below concerning resistance management. |
| Leverage 360 (premix of beta-cyfluthrin and imidacloprid) | 2.8-3.2 oz | See comments below concerning resistance management. |
* Pyrethroids might include Asana XL, Baythroid XL, Brigade (bifenthrin), Declare, Karate Z, Mustang Max and others. With the possible exception of bifenthrin products, do not expect synthetic pyrethroids to give adequate control of tarnished plant bugs if used alone.
Several premixes such as Brigadier, Leverage and Endigo contain a neonicotinoid component (imidacloprid or Centric). UT suggests avoiding further use of neonicotinoid insecticides after first bloom as a resistance management tactic to preserve this class of chemistry. However, you might consider their use if neonicotinoid insecticides have not been used for several weeks, thus not exposing consecutive generations to the same mode of action.